Creating websites that everyone can use isn't just a legal or ethical responsibility — it's good design. Accessibility ensures that everyone, regardless of ability, can interact with digital content effectively. Whether you're auditing an existing site or building something new, the following resources will help you understand best practices, run accessibility tests, and stay aligned with current standards such as WCAG 2.2.
⭐️ Pro tip: Look out for the items marked with a star — they're great starting points if you're new to accessibility or just want to focus on the essentials.
How to Use This Guide
I've organised these resources into categories so you can find what's relevant quickly. From community-led sites and official guidelines to testing tools and contrast checkers, this guide is both a learning resource and a practical reference for developers, designers, and content creators aiming to build more inclusive digital experiences.
I've been collecting accessibility resources for over seven years, and this post will continue to evolve as I discover new tools and updates.
Accessibility Checklist
Start by familiarising yourself with accessibility standards and checklists. These will help you evaluate your content and identify common issues early before they become bigger problems.
- ⭐️ The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): A detailed checklist based on WCAG, providing guidelines for creating accessible web content.
Accessibility Guidance
Community and Official Resources
Community-Driven Resources
- ⭐️ The A11Y Project: A community-driven resource that makes accessibility easier to understand and apply.
- A11y Coffee: Practical tips and advice for web accessibility.
Official Documentation
- ⭐️ MD Accessibility: Mozilla Developer's guide to web accessibility.
- Understanding WCAG 2.0: The official documentation explaining the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
- Web Accessibility Tutorials: Step-by-step tutorials from the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI).
Articles and Tutorials
These give background, techniques, and practical tips to bring accessibility into your workflow.
Introduction to Accessibility
- Accessibility (W3C): An overview of the standards that shape accessible web design.
- Handling common accessibility problems: Mozilla's guidance on solving common accessibility issues.
Keyboard Accessibility
- ⭐️ Keyboard Accessibility: A detailed walkthrough for making sites keyboard-friendly.
- Keyboard (MDN): Mozilla's advice on keyboard accessibility standards.
ARIA and Screen Reader Guidance
- Accessibility features in Firefox: How Firefox supports accessibility features
- ARIA in HTML: The official W3 guide to using ARIA roles and labels effectively
Testing Standards & Case Studies
- ⭐️ SSA 508 Test Method: The Social Security Administration's accessibility testing approach.
Insights and Case Studies
- What we found when we tested tools on the world's least-accessible webpage: GOV.UK's insights from testing accessibility tools.
- This guide is unreadable: A cautionary tale about poor accessibility practices.
Free Tools
Automated and manual testing tools can save time and highlight accessibility barriers. While no tool can replace human testing, these are some of the most reliable free options available.
Browser Tools
Testing and Evaluation Tools
- ⭐️ Lighthouse: A free, open-source audit tool from Google.
- Axe: One of the most popular accessibility testing libraries.
Browser Extensions
- ⭐️ Accessibility Insights: Microsoft's extension for finding and fixing accessibility problems.
- ARIA DevTools (Firefox) / (Chrome): View missing ARIA labels, misused roles, and keyboard issues.
- WAVE Evaluation Tool (Firefox) / (Chrome): WebAIM's easy-to-use browser extension for visual accessibility checks.
Standalone & Web-Based Tools
- Pa11y: Command-line tool for automated accessibility testing.
- Asqatasun: Open-source tool for automated accessibility testing.
Contrast and Visual Tests
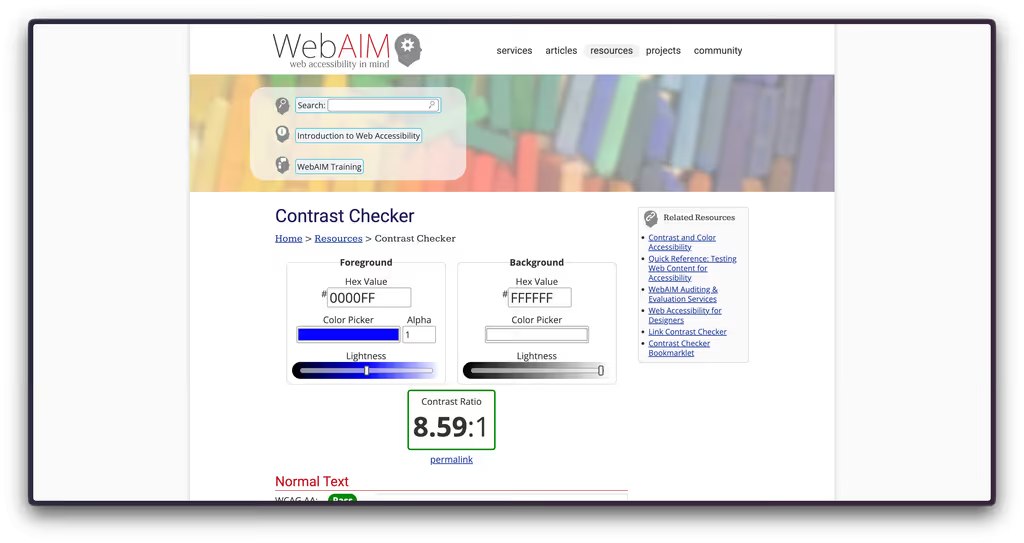
- ⭐️ Contrast Checker: Quickly see if text and background colours meet accessibility standards.
- Colour Contrast Accessibility Validator: An alternative for contrast checks.
Visual Accessibility Testing
- ⭐️ WAVE: One of the most widely used visual accessibility evaluation tools.
- HTML_CodeSniffer: Detects code-level issues.
- tota11y: A JavaScript library that visualises accessibility errors directly on your webpage.
Final Thoughts
Getting started with accessibility can feel overwhelming at first, but even small, consistent steps make a difference. The key is to keep learning, testing, and listening to the people who will actually use your digital content. Accessibility isn't about ticking boxes — it's about creating better experiences for everyone, regardless of ability.
Don't be discouraged by the technical challenges; it's a journey of ongoing improvement. Use the tools and resources above as your allies, and don't hesitate to seek feedback from users or fellow developers. The more inclusive your approach, the more your work can truly make a positive impact.
In the end, accessibility benefits us all. When we design with everyone in mind, we create websites, apps, and digital spaces that are more usable, welcoming, and effective. Keep at it — every bit of effort counts.
— Karl
